How 3D Printing Services are Revolutionizing PCB Design and Assembly
In recent years, the integration of 3D printing technology into PCB design and assembly has marked a transformative shift in the electronics industry. This innovation offers unparalleled benefits, including rapid prototyping, enhanced customization, and cost savings. By exploring how 3D printing services of OurPCB are reshaping PCB manufacturing, we can better understand their profound impact on the future of electronics.
The Convergence of 3D Printing and PCB Manufacturing
Traditional PCB manufacturing involves a series of complex steps, often requiring significant lead times and substantial financial investment. According to a report by the IPC (Association Connecting Electronics Industries), traditional PCB prototyping can take anywhere from two to eight weeks. In contrast, 3D printing can reduce this time to just a few hours, enabling faster design iterations and more efficient workflows.
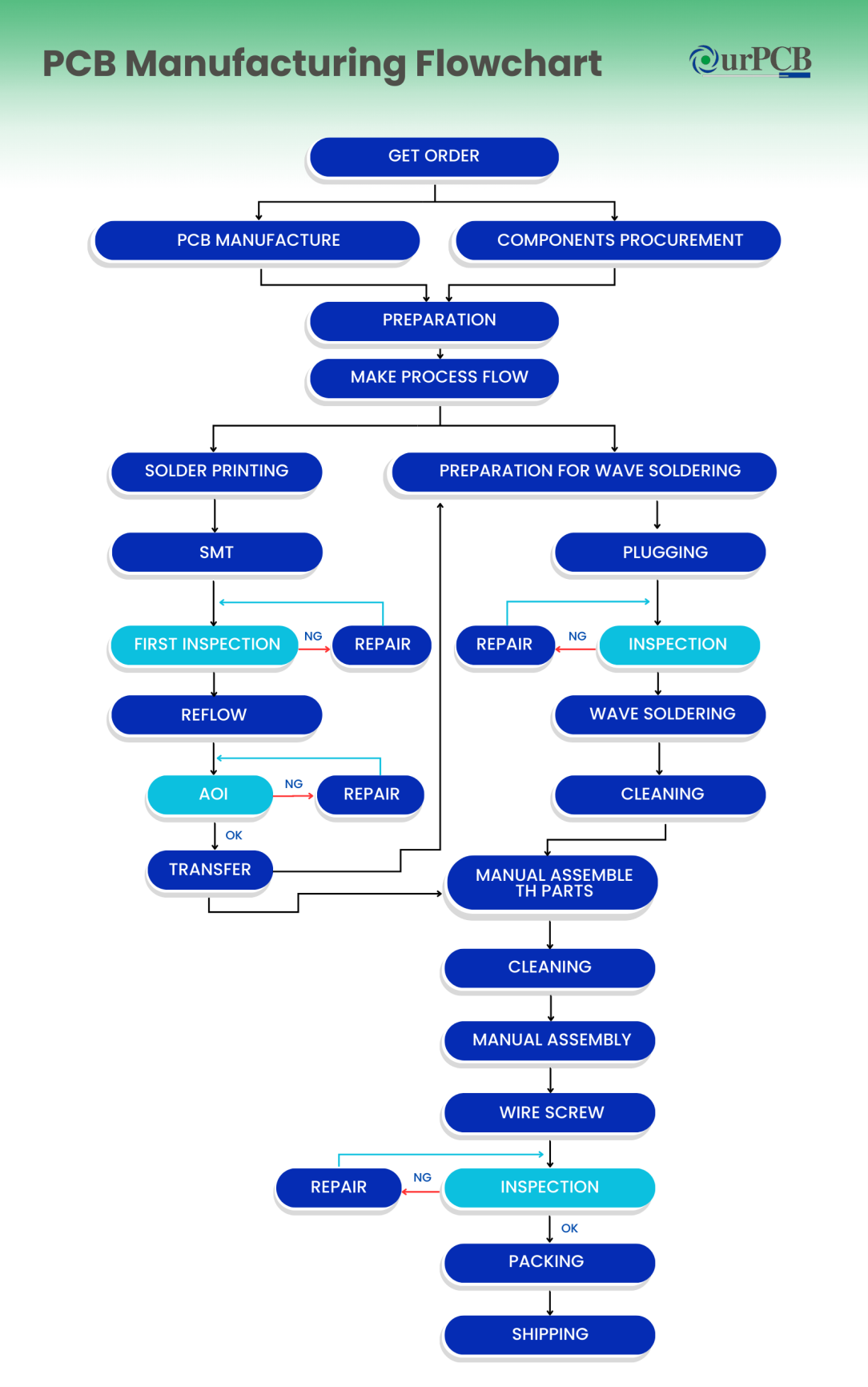
PCB manufacturing Processes
Rapid Prototyping: Speeding Up Innovation
One of the most significant advantages of 3D printing in PCB design is rapid prototyping. By utilizing 3D printing, engineers can quickly create prototypes to test and validate designs before committing to mass production. For instance, a study from Deloitte highlighted that companies leveraging rapid prototyping can reduce product development time by up to 50%. This acceleration allows teams to iterate on designs, test performance, and gather feedback without the lengthy delays associated with traditional methods.
Real-World Example: Medical Devices
In the medical device sector, rapid prototyping has proven invaluable. For example, researchers at MIT used 3D printing to develop custom surgical tools that integrate PCBs for monitoring and control. By producing prototypes quickly, they could refine designs based on surgeon feedback, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Enhanced Customization: Meeting Unique Needs
3D printing services allow for unprecedented customization in PCB design. Traditional manufacturing often involves tooling changes for each new design iteration, making it costly and time-consuming to accommodate unique specifications. In contrast, 3D printing enables designers to create tailored components, enclosures, and even entire PCBs that fit specific applications.
A survey by the International Data Corporation (IDC) found that 85% of manufacturers believe that custom products are essential to their success. With 3D printing, companies can easily produce low-volume, specialized PCBs without incurring exorbitant costs.
Real-World Example: Consumer Electronics
Take, for example, the development of custom casings for consumer electronics. Companies like Apple have begun using 3D printing for prototyping enclosures and components. This approach not only accelerates the design process but also allows for unique designs that enhance product aesthetics and functionality.
Cost-Effectiveness: Reducing Production Expenses
While the initial setup for 3D printing may require an investment, the long-term savings can be substantial. Traditional PCB manufacturing often incurs high costs due to tooling, setup, and material waste, particularly for low-volume runs. A study by Wohlers Associates estimated that 3D printing could reduce material costs by up to 70% compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
By adopting 3D printing, companies can produce only what they need, minimizing waste and storage costs. This shift is especially beneficial for startups and smaller companies that may not have the resources for large-scale production.
Real-World Example: Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, companies like Ford have implemented 3D printing to create prototype components for electronic systems. By using 3D-printed parts in the design phase, Ford reported savings of up to $100,000 per prototype project, showcasing how significant cost reductions can be achieved through this technology.

3D printed part
Complex Geometries: Pushing Design Boundaries
3D printing excels at producing complex geometries that are often impossible or cost-prohibitive with traditional manufacturing methods. This capability allows engineers to integrate various components directly into the PCB design, simplifying assembly and enhancing performance. According to a report by Gartner, over 30% of all 3D-printed parts will be used in the electronics sector by 2025.
Real-World Example: Aerospace Applications
In aerospace, companies like Boeing have leveraged 3D printing to create intricate electronic housings that include built-in connectors and thermal management features. This integration not only reduces the number of parts needed but also minimizes assembly time and potential points of failure.
Testing and Validation: Early Problem Detection
The speed of 3D printing facilitates earlier testing and validation in the product development lifecycle. By quickly producing multiple iterations of a design, engineers can test various configurations under real-world conditions. This iterative approach leads to better final products and significantly reduces the risk of costly errors during mass production.
A report from McKinsey indicates that early testing can reduce late-stage project failures by as much as 70%, underscoring the importance of rapid iteration in product development.
Sustainability: A Greener Approach
As environmental concerns grow, sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in manufacturing decisions. 3D printing offers a more eco-friendly alternative to traditional methods by minimizing material waste. The additive nature of 3D printing means that material is used only where needed, significantly reducing excess.
Additionally, advancements in biodegradable and recyclable materials for 3D printing are enhancing its appeal in environmentally conscious markets. According to a study by the World Economic Forum, sustainable practices in manufacturing could result in savings of up to $630 billion annually by 2030.
Challenges and Considerations
While the advantages of 3D printing are compelling, there are challenges to consider. Material limitations and print resolution can affect the quality of the final product. Moreover, companies must invest in training and development to ensure that their teams can effectively utilize this technology.
Conclusion
3D printing services are revolutionizing PCB design and assembly, offering significant benefits in speed, customization, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability. As industries continue to embrace this technology, it will play an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of electronics.
For companies looking to stay competitive in the fast-paced electronics landscape, integrating 3D printing into their PCB manufacturing processes is not just an option—it’s becoming a necessity. Whether you are a startup developing innovative solutions or an established player aiming to enhance your offerings, leveraging 3D printing can lead to groundbreaking advancements in PCB design and assembly. The future is here, and it’s 3D printed.