Data Analytics vs. Data Science: A Comparative Guide
Big data has now established itself as a critical element of the IT industry because it can offer businesses insightful information and beneficial results. However, creating such massive databases necessitates knowledge and access to the tools necessary to sift through them and reveal accurate information. To better understand big data, data science and data analytics have moved beyond their traditional roles as primarily academic disciplines to become crucial components of business intelligence and big data analytics platforms.
However, it might be challenging to distinguish between data analytics and data science, even though the two use different tactics and get different results. If you need to analyze the data generated by your company, you must comprehend what each of them brings to the table and how they differ.
To get the most out of your big data analytics, we examine both groups, evaluate their differences, and highlight their advantages.
Table of Contents
What Exactly Is Data Science?
Data science is an interdisciplinary field that searches through enormous amounts of structured and unstructured data for valuable insights. Data scientists’ primary objectives are to pose questions and suggest potential lines of inquiry, focusing less on giving precise solutions and more on selecting the appropriate research questions.
A significant field focus is finding solutions to problems we do not even realize we do not understand. A range of techniques, including computer science, predictive analytics, statistics, and machine learning, are used by data scientists to search through massive datasets to find solutions to problems that have not yet been identified. Experts accomplish this by identifying potential trends, investigating numerous unrelated data sources, and developing more efficient data analysis methods.
What Skills Are Required of a Data Scientist?
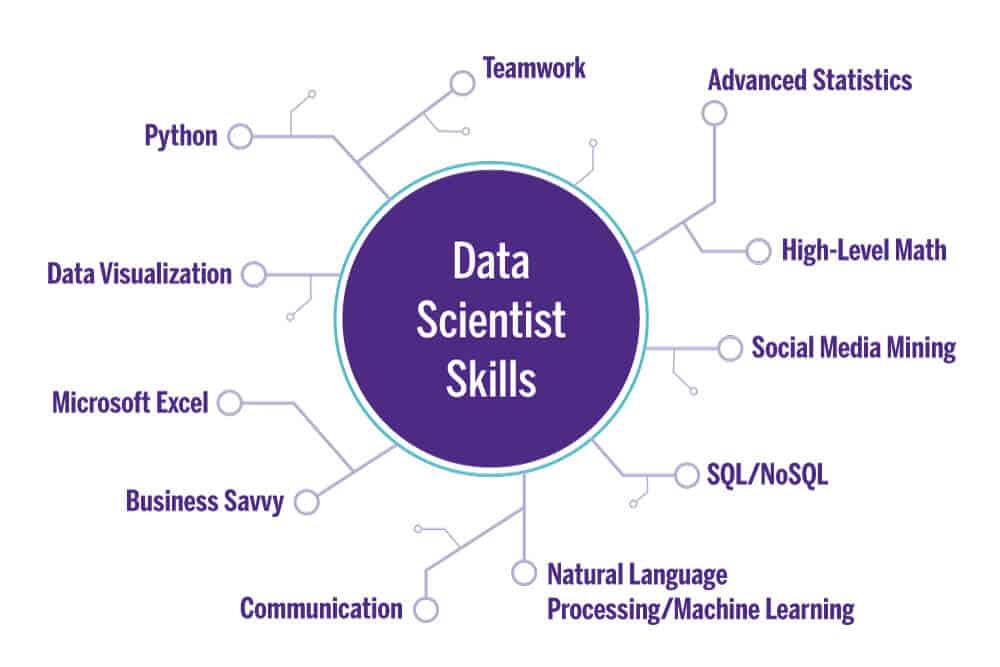
Anyone looking to start their career in data science should focus on three areas: analytics, programming, and domain knowledge. Going a step further, the following abilities can support your development as a data scientist:
- Working knowledge of unstructured data from various sources, including social media and video, and proficiency in Python, SAS, R, and Scala.
- Recognize various analytical methods.
- Understanding of machine learning
Advantages of Data Science Education
Data science is more concerned with broad data insights than particular query solutions. Usually a subset of data science, data analytics is more specialized and less concerned with the big picture. There are several reasons why data science professionals might decide to save analytics for later in their careers. Consider the following advantages of first understanding data science:
- You will have more freedom in your work and be able to pick up analytics quickly.
- Become more adept at understanding fundamental mathematical ideas.
- This leads to several important conclusions, one of which is that if you want to understand data science initially, you must feel comfortable dealing with sizable amounts of unstructured data.
- Learning programming languages is a good idea through data science.
- A data science certification will give you more freedom in the future.
- The collaboration of data across disciplines will become more familiar to you.
- Although those new to working with data are best suited for learning about data analytics, it is worthwhile to learn more if you have professional experience in data science.
What Exactly is Data Analytics?

Basic descriptive statistics, data visualization, and communicating data points for conclusions are all typical competencies of a data analyst. To the same extent as data analytics, data science is required. They must have a thorough understanding of databases, a solid grasp of statistics, the ability to create new views, and the ability to visualize data.
Using advanced techniques in data science services can significantly enhance these capabilities, providing sophisticated tools for comprehensive data analysis and interpretation.
What Skills Are Required for a Data Analyst?
Key business stakeholders should be able to speak with a data analyst about the data for a specific topic or query. If you want to work as a data analyst, you must be able to master the four skills listed below:
- Understanding of statistics and mathematics.
- Command of Python and R.
- tampering with data
- Determine PIG/HIVE.
Advantages of Data Analysis Education
Before entering the field of data science, it is advantageous to become knowledgeable about data analysis. The following are a few of the initial advantages of learning data analytics:
- Knowing how to evaluate data will be helpful if you want to work in data science.
- It will get easier for you to express yourself verbally and draw better pictures.
- Your ability to collaborate with stakeholders may get better.
- Learning more about exploratory data analysis
- Your ability to influence feature development will grow.
- Every data professional ought to have the ability to analyze data.
- The most popular processing languages used by analysts are R and Python. However, understanding processing languages is advantageous for any data professional.
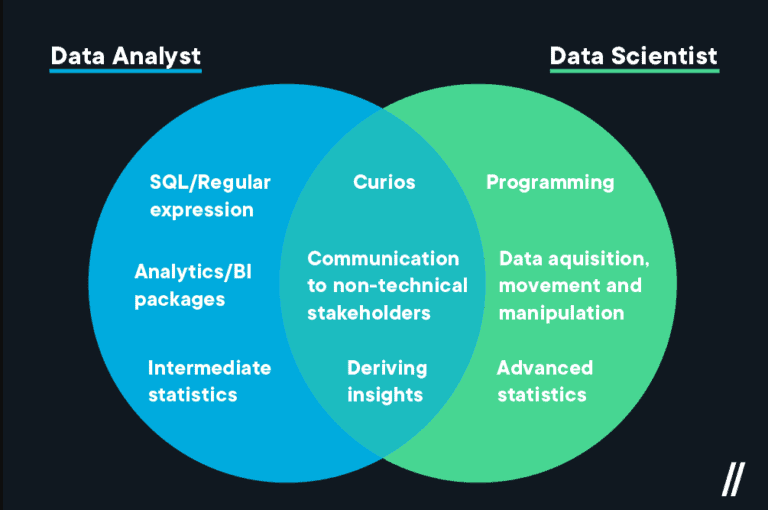
Similarities Between Data Science and Data Analytics
Both fields strongly emphasize STEM and are in high demand across numerous industries. There are many similarities between data science and data analytics. Both utilize data to support decision-making by facilitating an understanding of an organization’s operations.
Here are a few examples of where the two fields intersect.
Massive Amounts of Data
When working with large data sets, analytics and data science professionals analyze millions of data points. The accuracy of any study depends on the ability to wrangle (clean), maintain, and organize the potentially low-quality data that may be present in these enormous databases.
Successful Communication
Data analysts and scientists work together with individuals from various professions who require more technical backgrounds. These experts are accountable for effectively and succinctly communicating their findings.
Technical Proficiency
Programming skills (in R, Python, Tableau, and SQL), statistics, Excel, data visualization, and modeling are prerequisites for both professions. These professionals must approach project management problem-solving with a high level of analytical rigor.
Differences Between Data Analysts and Data Scientists

Data scientists create new methods for gathering and analyzing the data that analysts might use, whereas data analysts analyze the already available data. If you enjoy math, statistics, and computer programming, this might be a great career choice.
Data Scientists vs. Data Analysts: Competencies
Although data analysts and data scientists have some skills in common, there are also many differences between the two job roles.
Skills for Data Scientist
- Cloud computing and artificial intelligence
- Power BI is used for data visualization, whereas Tableau is used for narrative.
- Proficient in SQL, Python, R, MATLAB, SAS, and Spark.
- Firm mathematical grounding in calculus, linear algebra, and statistics
- Modification and data manipulation
Skills for Data Analysts
- Generating Tableau reports and analyzing data in MS Excel
- Outstanding statistical and probability knowledge.
- Information manipulation
- Programming knowledge in Python and SQL is required.
- Examine the information.
Data Analyst vs. Data Scientists: Responsibilities
Data Analyst’s Duties
- Gathering, filtering, and cleaning data from various databases and storage locations is necessary.
- Using Excel and BI tools, create various reports with charts and graphs.
- Analyze large datasets for patterns and trends.
- Relational database management systems (RDBMS) like MS SQL Server, Oracle DB, and MySQL allow you to save, change, and retrieve data using complex SQL queries and scripts.
Data Scientist’s Duties
- You can build AI models by fusing several algorithms and built-in libraries.
- Massive amounts of structured and unstructured data can be gathered from various sources using ad hoc data mining.
- Machine learning models can be used to automate tedious tasks and produce insights.
- Create and assess complex statistical models from enormous data sets using a variety of statistical methodologies and data visualization techniques.
Data Scientists vs. Data Analysts: Salaries
The highest-paid professions overall are data scientists and analysts. According to Glassdoor, the annual salary for a data scientist in the United States is $120,800. At the same time, the average pay for a data analyst in the United States is over $70,500. Regarding pay, a data analyst earns an average yearly salary of 8 lac rupees in Asia. On the other hand, a data scientist typically earns 13 -lac rupees per year.
Data Scientist vs. Data Analyst: Education
It’s only sometimes necessary for data scientists and analysts to hold advanced degrees. You must have a bachelor’s degree in any relevant field in addition to an engineering degree in computer science, information technology, electrical engineering, or mechanical engineering. A Ph.D. in math, statistics, or economics is a different option. It is crucial to have expertise in the field in which you work or the position you seek. Without a master’s degree, you can advance your career as a data analyst or scientist.
Engineering jobs are essential in the realm of data science and analytics, as positions in computer science, information technology, electrical engineering, or mechanical engineering provide the foundational skills necessary to excel without necessarily requiring advanced degrees.
Data Scientist vs. Data Analyst: Career Advancement
Data science is utilized in almost every industry, including manufacturing, logistics, e-commerce, and healthcare. Companies need help locating qualified data scientists to develop algorithms and produce predictive models because they believe this position has a skill gap. Data scientists are in short supply globally, and businesses are looking for experts who can use data to make critical decisions and accelerate business growth. This challenge highlights the importance of leveraging advanced solutions like data catalog tools, which help organize and streamline access to vast datasets, enabling faster and more accurate decision-making.
On the other hand, it would be best if you worked as an entry-level data analyst to launch an analytics career. You will conduct database searches, use BI tools to produce reports, and evaluate significant data based on your current understanding. By leveraging tools such as a dbt IDE (Integrated Development Environment), you can streamline your data analysis workflows and efficiently transform raw data into actionable insights. You will find it simpler to understand how to conclude accurate business data. You can advance your career by striving to become a senior data analyst or consultant by learning sophisticated data analytics techniques and applying mathematics.
If you possess the necessary skills, domain knowledge, and business acumen, you can be successful as a data scientist. There are lots of chances to develop and work in research science.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans: Analysts and data scientists are both in high demand. These fields are in high demand among working adults and college students. A data scientist role is suggested for those who wish to construct intricate machine learning models and utilize deep learning to assist in the execution of human activities. A position as a data analyst is more appropriate for those who want to begin a career in analytics.
Ans: Data scientists are among the highest-paid professionals in the field. In the United States, a Data Scientist makes around $130,080 a year compared to a Data Analyst’s $75,000.
Ans: Yes, a data analyst can advance to the position of data scientist by mastering programming, honing their mathematical and analytical abilities, and learning about machine learning methods.
Ans: Data analysts must be able to code to modify and alter data. It is optional for them to possess highly developed coding abilities.
Ans: Data scientists and analysts use programming to organize, process, and analyze data. These people also produce business reports using BI tools like Excel and Tableau. Furthermore, data scientists and analysts are experts at transforming and presenting data.
The Final Words
Both professions are becoming more critical to businesses across all industries, so it might be beneficial to learn about them. Data science and data analytics are similar in many ways, but it can take time to determine which is more crucial in business. First, consider studying analytics to better prepare yourself for the demanding field of data science.
Which of the two data science and analysis disciplines will help you better understand the responsibilities and obligations of each role? When you know how to use your unique set of abilities, talents, traits, and passions to serve in a position where you will succeed, you can take a much faster and more direct path to the top.